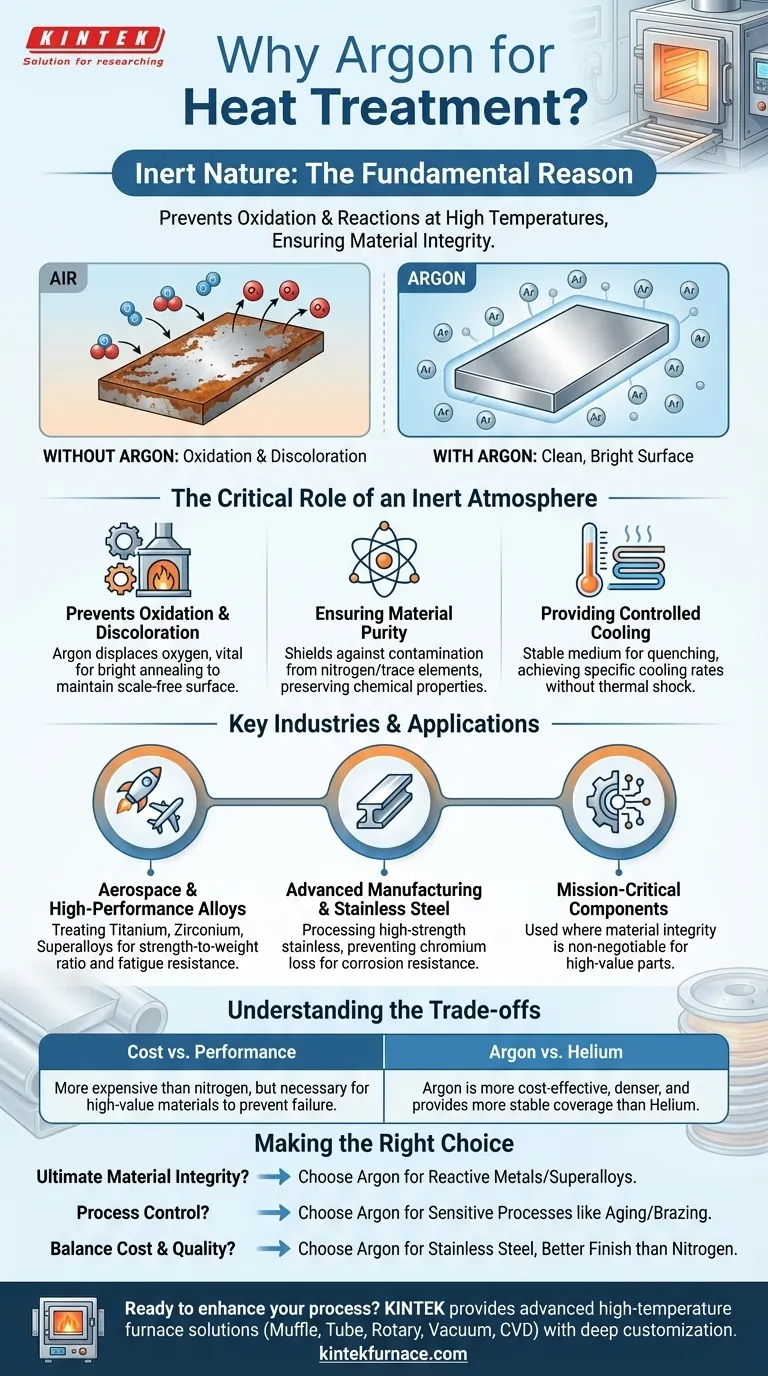
Argon is widely used in heat treatment across several industries due to its inert properties, which prevent oxidation and contamination during high-temperature processes. Key sectors include aerospace, automotive, high-performance alloys, advanced manufacturing, and healthcare. These industries rely on argon to maintain material purity, enhance mechanical properties, and ensure safety in processes like sintering, hot isostatic pressing, and vacuum heat treatment. Additionally, argon is essential in atmosphere retort furnaces for creating controlled environments that protect sensitive materials from reactive gases.

Key Points Explained:
-
Aerospace Industry
- Argon is critical for heat-treating turbine blades, engine components, and structural alloys.
- Prevents oxidation in high-temperature processes, ensuring fatigue resistance and durability.
- Used in vacuum furnaces and atmosphere retort furnaces for precision treatments like solution annealing.
-
Automotive Industry
- Enhances the hardness and wear resistance of gears, bearings, and transmission parts via carburizing or nitriding in argon-rich atmospheres.
- Supports lightweight alloy treatments (e.g., aluminum) for fuel-efficient vehicles.
-
High-Performance Alloys & Advanced Manufacturing
- Argon shields superalloys (e.g., Inconel) during sintering or hot isostatic pressing (HIP) to avoid grain boundary contamination.
- Vital for additive manufacturing (3D printing) to prevent porosity and cracking in printed metal parts.
-
Healthcare (Medical Devices & Implants)
- Ensures biocompatibility in titanium and stainless steel implants by preventing surface oxidation during annealing.
- Used in vacuum heat treatment for surgical tools to maintain sterility and precision.
-
Other Key Applications
- Powder Metallurgy & Ceramics: Argon aids in sintering compacted powders without chemical degradation.
- Energy Sector: Protects solar cell components and battery materials during thermal processing.
Why Argon?
- Chemically inert, making it ideal for reactive metals (e.g., titanium, magnesium).
- Replaces oxygen to eliminate decarburization in steel treatments.
- Acts as a safety buffer in furnaces by purging flammable gases.
Have you considered how argon’s role in heat treatment aligns with the growing demand for contamination-free materials in electric vehicles and space exploration? Its silent yet pivotal presence underscores its value in modern industrial advancements.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications of Argon |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, engine components, structural alloys (prevents oxidation) |
| Automotive | Gears, bearings, lightweight alloys (enhances hardness & wear resistance) |
| High-Performance Alloys | Superalloys (Inconel), additive manufacturing (prevents contamination) |
| Healthcare | Titanium implants, surgical tools (ensures biocompatibility & sterility) |
| Energy & Ceramics | Solar cells, battery materials, powder metallurgy (protects during sintering) |
Upgrade your heat treatment processes with precision argon solutions!
KINTEK’s advanced vacuum and atmosphere furnaces are engineered for industries demanding contamination-free results. Whether you're in aerospace, medical devices, or additive manufacturing, our deep customization capabilities ensure your materials meet exact specifications. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace systems can optimize your production.
Products You Might Be Looking For:
High-vacuum observation windows for real-time process monitoring
Precision vacuum feedthroughs for sensitive applications
Vacuum hot press furnaces for advanced material consolidation
Stainless steel vacuum valves for reliable gas control
MPCVD systems for diamond synthesis and coatings
Guia Visual
Produtos relacionados
- Forno de atmosfera inerte de azoto 1700℃ controlado
- Forno de atmosfera controlada de correia de malha Forno de atmosfera inerte de azoto
- Forno de atmosfera inerte de azoto controlado de 1400℃.
- Forno de atmosfera inerte de azoto controlado de 1200℃.
- Forno com atmosfera inerte controlada de azoto e hidrogénio
As pessoas também perguntam
- Qual é o mecanismo pelo qual uma atmosfera redutora melhora o desempenho da ferrite de Mn-Zn? Desbloqueando a Excelência Magnética
- Por que a escolha da atmosfera do forno depende do processo e material específicos? Garanta Resultados Ótimos de Tratamento Térmico
- Qual é o propósito de usar um forno de pré-sinterização com fluxo de argônio? Proteger a integridade do Hastelloy-X
- Quais são os principais tipos de atmosferas de fornos à base de nitrogênio? Otimize Seu Processo de Tratamento Térmico
- Como um forno de caixa com atmosfera suporta a síntese de materiais de nova energia? Desbloqueie o Controle Preciso para Materiais de Alto Desempenho
- Como o forno de atmosfera de recozimento tipo caixa gera calor? Domine o Controle Preciso de Temperatura para o Seu Laboratório
- Qual é o papel de um forno de sinterização em atmosfera no processo MLM? Preparação de Compósitos Mestre CNT/Cu
- Como fornos de aquecimento de alta precisão e proteção com nitrogênio contribuem para o HTXRD? Otimize sua análise in-situ



















